POSITIONS ON THE EARTH GLOBE
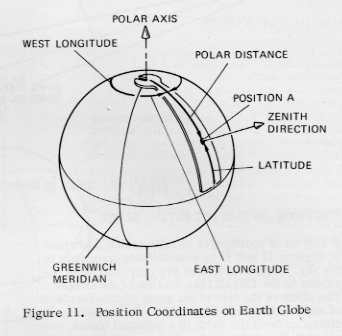
The system described in Figure 9 is used with the EARTH GLOBE, as shown in Figure 11. The polar distance is the angle between the polar axis and the zenith direction at Position A. The complementary value, called LATITUDE is the angle distance from the equator to Position A. Latitude equals 90° - polar distance and is North or South of the equator.
The measurement between meridians on the earth globe is called LONGITUDE, and is referenced to the Prime or Greenwich Meridian, which passes through both poles and Greenwich, near London, England. Longitude is specified as either West or East longitude, depending on whether the direction lies West or East of Greenwich. Conventionally, the maximum longitude vale is 180 W or E. The maximum latitude vlaue is 90° N or S.
This system of coordinates permits precise description of any point on the surface of the earth globe, using the reference points noted.
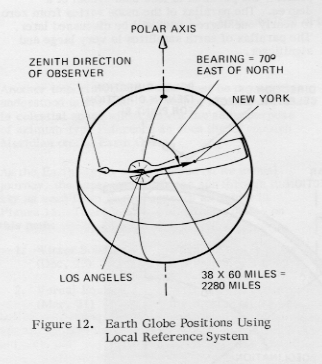
The system described in Figure 10 of referring positions to the observer is also used on the earth globe. Refer to Figure 12. The spanner is used to measure the azimuthal angle (bearing) from North to another point on the globe. In the figure, New York lies 70° E of N as viewed from Los Angles. The spanner can also be used to determine actual linear distance along the great circle between the two points. In this case, New York lies 38 divisions or degrees from Los Angeles. Each division on the spanner represents 60 nautical miles, therefore New York is 38x60=2280 nautical miles from Los Angeles.
EXCERCISES
1. Measure the distance from New Orleans to Port Guinea (on the W. Coast of Africa). What is the bearing?
Answer: 4800 mi., 6° N of East.
2. Measure the distance from Port Guinea to Moscow. What is the bearing?
Answer: 45000 mi., 30° E of North.
3. Measure the bearing from London to Mecca. (20° N, 39° E).
Answer: 120° E of N.
Page 7